Today we’re going to talk about the plant life cycle. If you’re not familiar with the five stages of a plant’s life cycle and how those stages alternate, we will explain it all.
If you’re hearing the first time the terms such as seed dispersion, diploid cells, gametophyte phase, sporophyte phase, pollen sticks, and more, you will learn all about it now.
Through these several stages plant starts its new life from seeds to a mature plant. How does this cyclic process work and why is it important in the botanic world, let’s find out then.
At the very end, we bring you the FAQs section where we’ll talk about the full maturity of plants, reproduction, and generational alternation of plants.
Let’s find out how to “push” your plant to have a better life cycle so you have it the second summer in a row as well. Next time, your flower will be fresh and ready to bloom.
What Is A Plant Life Cycle?

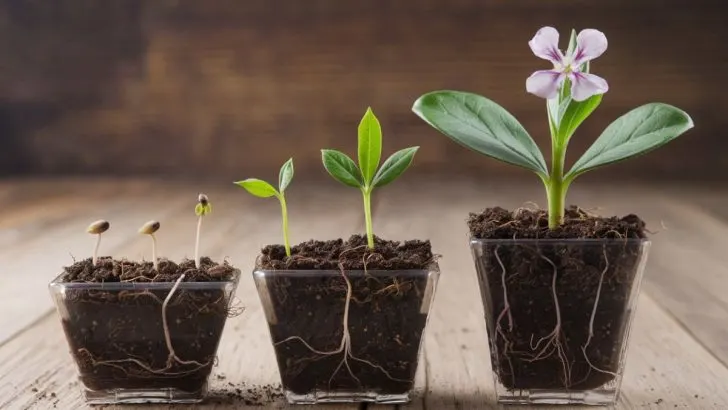
The life cycle of a plant is all the stages the plant goes through from the beginning of growth to death.
It’s usually mentioned the 5 main stages of a plant’s life cycle, but sometimes, many botanic authors mention more.
Stages Of A Plant’s Life Cycle
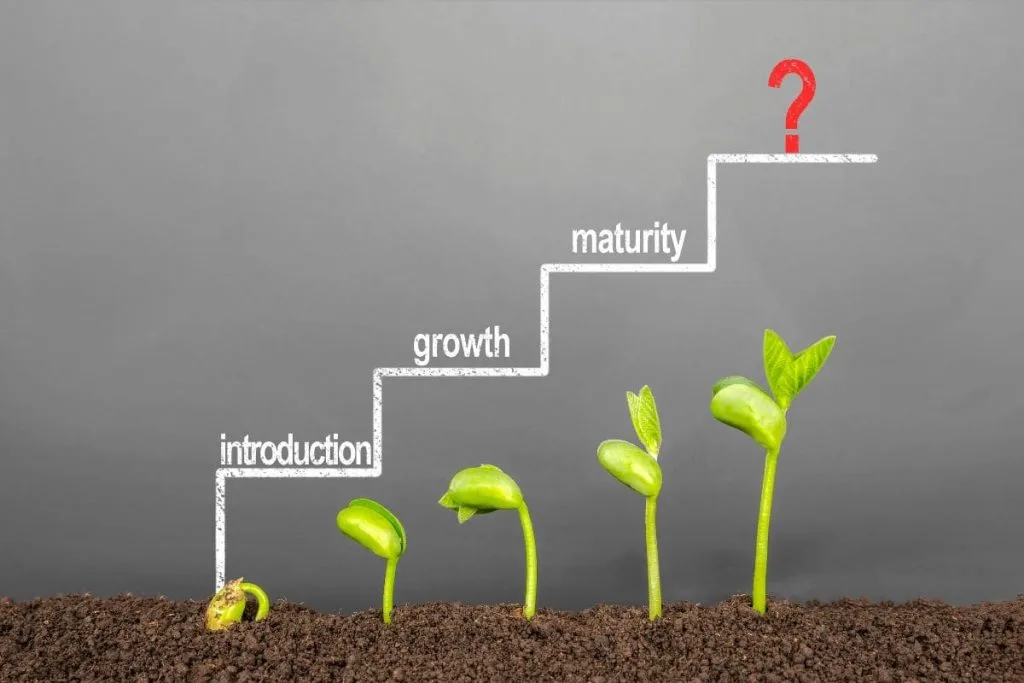

Plant describes mostly 5 phases of the life cycle of the plant. For the same species of plant, this is the same, but for different types of plants and flowers, the life cycle is sometimes a bit different.
Below, we will talk about a plant’s life cycle in detail. Life cycles also depend on how a seed germinates and in what kind of conditions the seed begins to grow-develop.
Plant Life Cycle Phase: Seeds
The first and initial process of a plant’s life cycle is the setting of seeds. In order for the next step, ie sneezing, to occur, we must first have the material for it, in this case, the seeds.
Sometimes we can get the seeds from the same plant – for example, the velvet plant, and sometimes we can buy them. Experienced botanists will tell you that these seeds are better because they are more “preserved”, but that doesn’t matter if the plant is grown in good conditions.
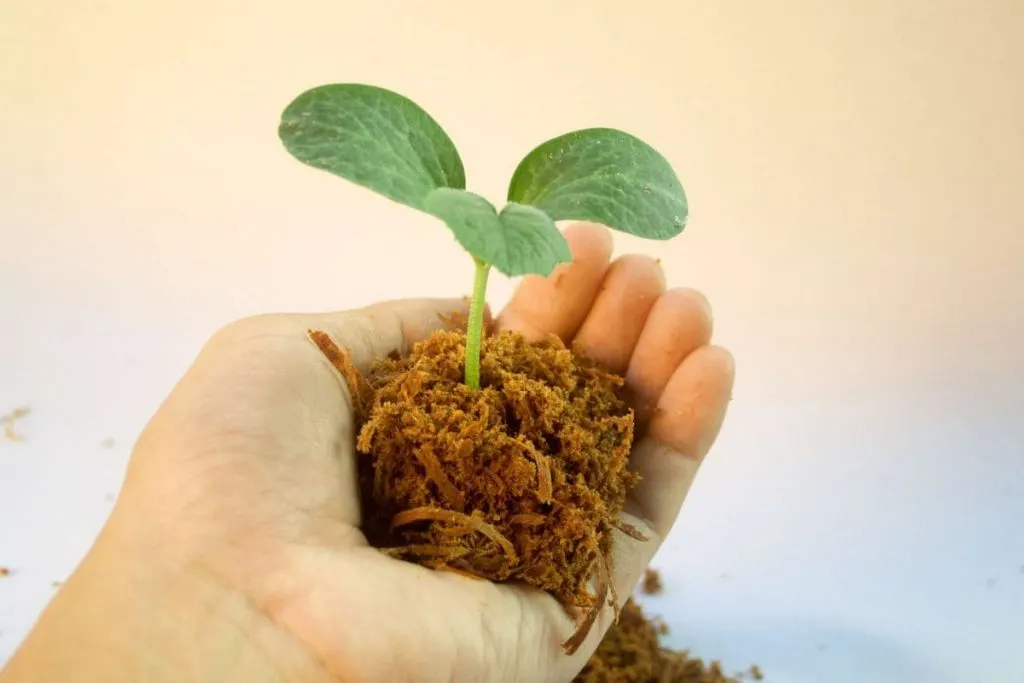
Plant Life Cycle Phase: Seed Germination And Seedling
In order for the plant to germinate, you need to keep it in water or adequate soil for a while and expose it to direct sunlight in the morning and mild light in the afternoon.
Germination is actually the process of developing a new plant from a seed. This is proof that your seeds are good and favorable for the growth of a new plant.
At these times, the plant also needs heat, so this is not done in winter. When the plant germinates, then you can set up a seedling for it, in which you will plant it and fix it so that it continues to grow and develop.
The germination process is completed when small leaves appear on the new plant, which later develops into a larger plant.
Plant Life Cycle Phase: Mature Plant
The plant is mature when its roots are fully formed and when its leaves grow completely. Usually, on one seedling, the plant has 3 or 4 leaves depending on the species. This is one of the indicators that the plant is ripe.
Plant Life Cycle Phase: Flowering Plants
Usually in the spring, most plants flower, produce seeds and drop their leaves and seeds and enter a dormant or hibernation phase. These seeds mostly remain as a trace of former flowers on the pistil and pistil and await further spread.
Plant Life Cycle Phase: Dispersion Of The Seeds
Seed dispersal is done by bugs and insects usually in summer or early autumn (butterflies, bees, bumblebees, etc). This provides “supplies” of plants in nature and the development of the same plants without work and human hands.
What Are The Three Stages Of A Plant Life Cycle?
The three stages of a plant are:
- Seed stage – the steady phase when we plant the seeds.
- Growth stage – the process of growing our plant in its new pot.
- Reproductive stage – formed plant-mature plant is ready to reproduce.
What Are The Four Stages Of A Plant?
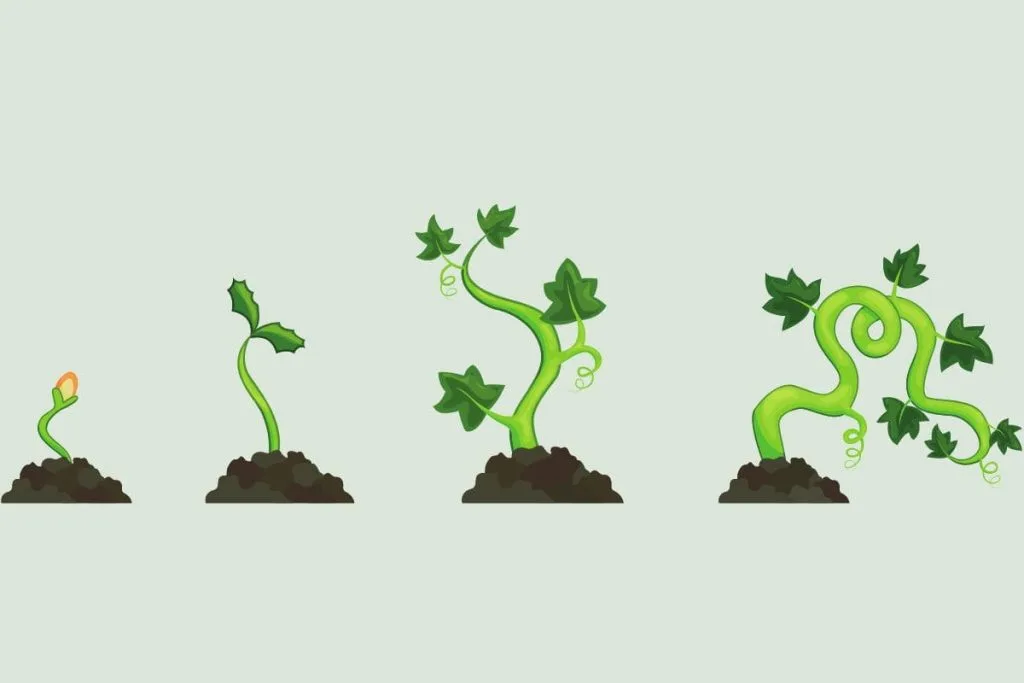

The four stages of a plant are:
- Seed – planting the seeds.
- Sprout – sprouting of a plant, ready for the transplant.
- Small plant – young plant in its early growth phase.
- Adult plant – mature plant ready to propagate.
What Are The Six Stages Of A Plant?
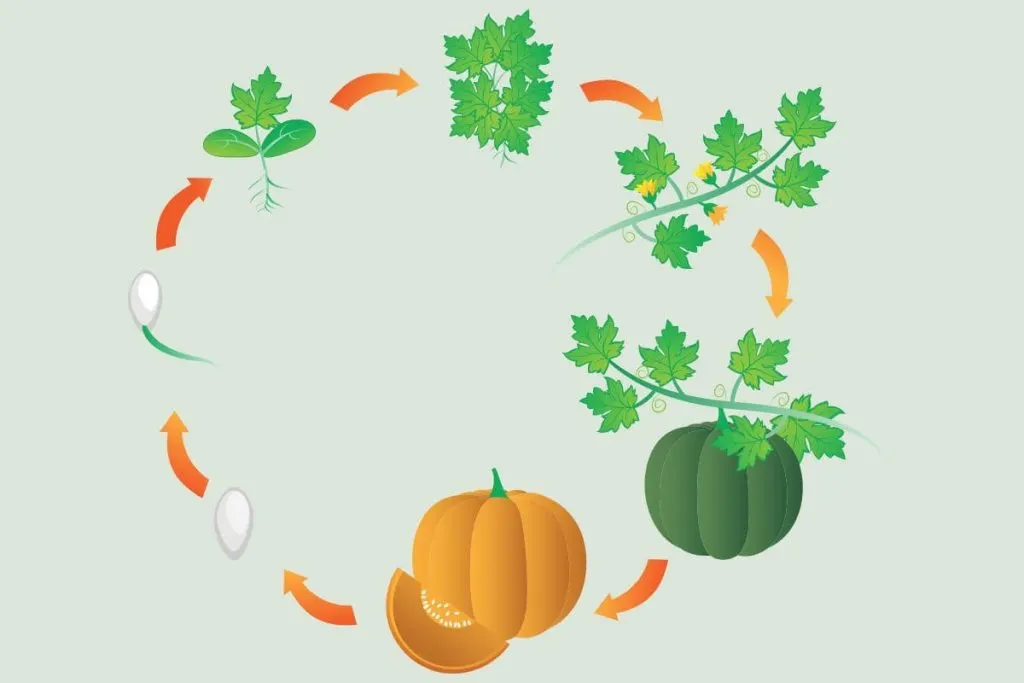

The six stages of a plant are:
- Sprout – the germination of a young plant that is ready for planting.
- Seedling – a new seedling where the plant will grow permanently.
- The vegetative phase – initial formation of leaves and flowers.
- Budding – the formation of flower buds where flowers will grow in the spring on the tops of the stems, the early stage of the plant’s maturity.
- Flowering – flowering, maturity of the plant.
- Ripening – a mature plant, usually after the flowering phase.
Popular FAQs On The Plant’s Life Cycle

Below we bring you the most popular questions about the plant’s life cycle. Let’s find out a bit about the plant’s life cycle before the end.
What Are Seedless Plants?
Seedless plants are plants that don’t have seeds nor need them for reproduction. The famous type of these plants are types of ferns indoors such as Japanese fern trees and others.
During evolution, these plants are one of the many plants that exist even today but don’t have seeds.
What Is Sexual Reproduction In The Plant Life Cycle?
The sexual reproduction of plants includes a haploid phase of reproduction. It is important for these reproduction cycles that plants have both male and female parts.
If they don’t, they won’t be able to produce seeds. Avoid doing this reproduction in cold temperatures as well.
Make sure the plants you’re using for this reproduction are parent plants, not young plants. The plant cycle during this process depends on the plant’s maturity.
What Is Asexual Reproduction In The Life Cycle Of Plants?
What Is Seed Germination?
Seeds germination is the process of germination of plants when they are primarily sown. In order for the germination phase to occur at all, the plant needs to be in adequate soil, sometimes in water, and needs a lot of light.
How Do Seedless Plants Reproduce?
They are propagated with water and roots. Plant growth depends on the conditions the plant is growing in much more than its way of reproduction.
New plants grow easily when propagated with water and the plants lifecycle lasts the same as with the other plants.
The only difference with these plants is that one plant needs more time to reproduce, develop flowers (leaves) and produce food as well.
How Are Plant Flowers Pollinated?
What Is Self-pollination?
Final Thoughts

In today’s article, we learned everything you need to know about the plant life cycle. If you have been wondering how processes in nature take place, you have no more reason to wonder.
We made sure to collect all the information for you and put it in one place – this article. Now, if you closely follow the development of your plant, you will notice changes in them and you will know which phase is passing and which is coming, and you will be better prepared for them.
We hope our article was helpful. That would be all for today. See you tomorrow with more similar topics.

