Planting by the calendar no longer works like it used to. With shifting seasons, late frosts, and sudden heat waves, guessing the “right time” often leads to stunted growth, failed crops, or replanting.
Instead of relying on dates, try using climate-proof timing strategies—methods based on real-time cues from your soil, weather patterns, and plants themselves. These indicators are far more accurate and adaptable, no matter where you live.
In this article, you’ll learn 17 proven techniques to stop planting on hope and start planting with confidence—so your garden stays resilient, timely, and productive, even in unpredictable conditions.
Understanding Local Microclimates

Every garden has its unique microclimate that can significantly impact plant growth. Urban areas, for example, might differ from rural settings due to concrete and lack of shade. By observing these small but significant differences, gardeners can tailor their planting schedules effectively.
Consider how wind patterns, sunlight exposure, and nearby structures affect your garden’s temperature. Observing these elements closely can reveal the best planting times for different plant varieties. Use these observations to adjust your planting timetable, ensuring each plant gets the best possible start.
Soil Temperature Monitoring
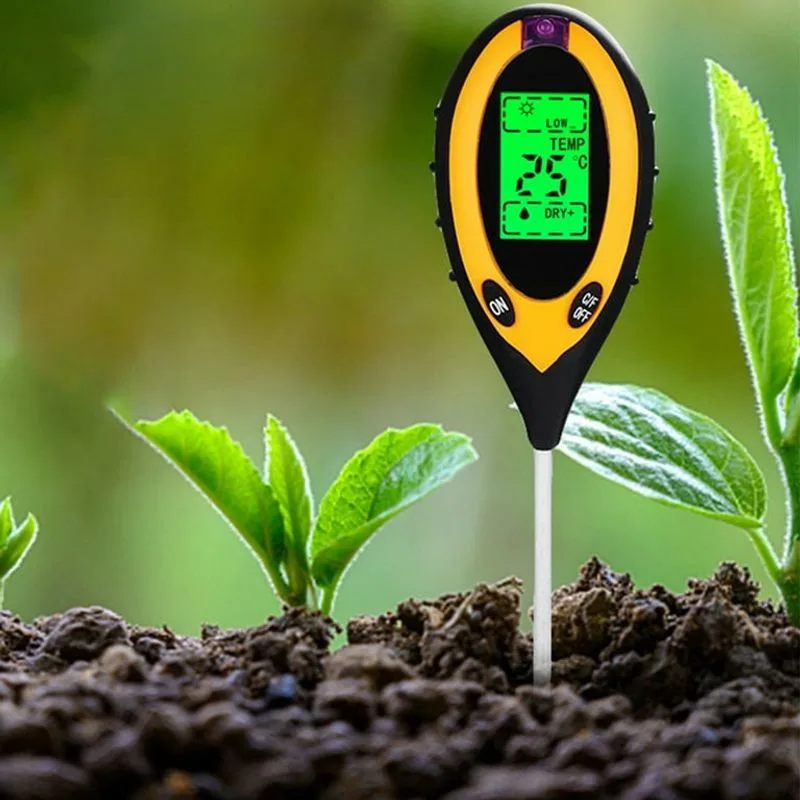

Soil temperature plays a crucial role in successful planting, as different plants have specific temperature needs for germination. Using modern tools like digital soil thermometers can provide accurate readings.
With this information, you can plant seeds at precisely the right time, avoiding the common pitfall of sowing too early or too late. This strategy ensures healthier, more robust plants. Accurate soil temperature readings take the guesswork out of gardening, allowing you to align planting with optimal growth conditions.
Phenology Observations

Phenology, the study of cyclic and seasonal natural phenomena, can guide planting decisions. By observing patterns like blooming times and bird migrations, gardeners can better predict favorable planting windows.
Keeping a phenology journal helps track these natural indicators. Aligning your planting schedule with these cues ensures that plants are sown under ideal environmental conditions. This method connects gardeners to nature’s rhythms, making planting more intuitive and effective.
Utilizing Weather Forecast Technology

Today’s technology offers advanced weather forecasting tools that can aid gardeners immensely. Smartphone apps and dedicated weather stations provide real-time updates, helping you plan gardening activities around anticipated weather changes.
By relying on accurate forecasts, gardeners can avoid planting during risky weather conditions like frost or heavy rain. This foresight can prevent crop failures and encourage more successful harvests. Technology bridges the gap between traditional gardening wisdom and modern climate realities.
Succession Planting Techniques
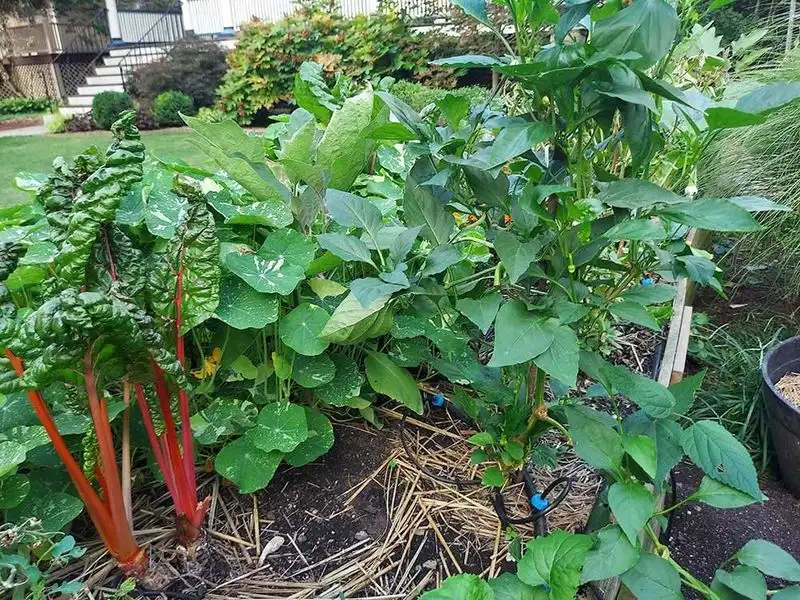

Succession planting involves sowing crops in intervals to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the season. This technique maximizes garden productivity and adapts well to changing climates.
By staggering planting dates, gardeners can reduce the risk of total crop failure and make better use of available space. As climatic conditions evolve, this flexible approach allows for adjustments in planting times, ensuring a steady supply of fresh produce. It’s a practical strategy that aligns with both traditional wisdom and contemporary challenges.
Frost Date Calculations
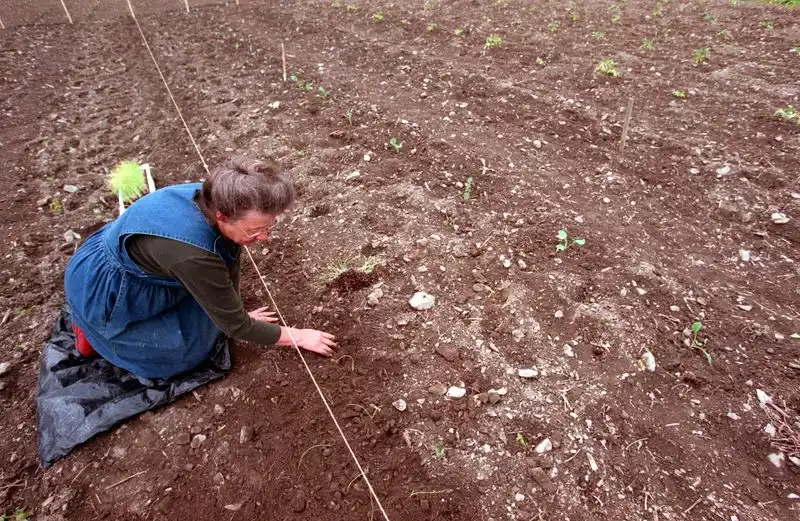

Knowing your area’s frost dates is essential for timing planting in both spring and fall. This knowledge helps in planning when to start seeds indoors and when it’s safe to transplant seedlings outside.
Calculating frost dates involves understanding local climate patterns and historical weather data. By aligning planting schedules with these dates, gardeners can protect young plants from unexpected frosts. This careful planning minimizes risks and enhances plant survival rates, making it a cornerstone of climate-proof gardening.
Native Plant Selection
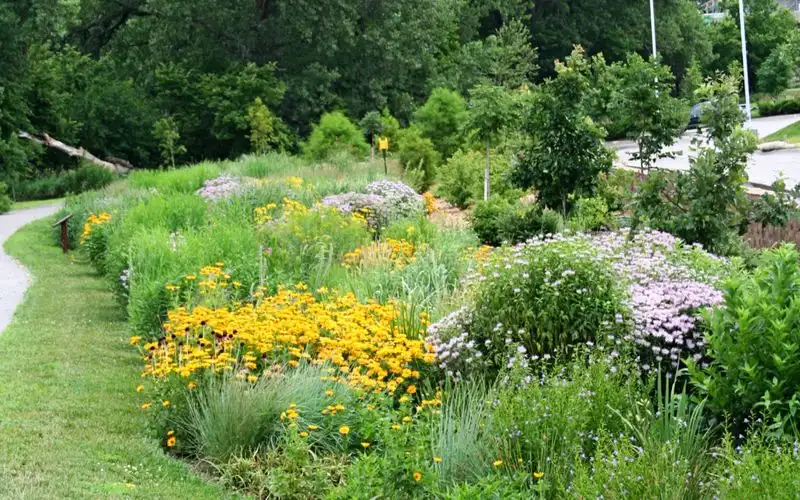

Native plants are well-adapted to local climate conditions, making them a smart choice for sustainable gardening. These plants typically require less water and care, as they are naturally resilient.
By selecting plants that thrive in your region, you create a garden that’s both beautiful and ecologically sound. This strategy not only supports local wildlife but also ensures your garden withstands changing climatic conditions. Embracing native plants aligns with eco-friendly gardening practices and promotes biodiversity.
Raised Bed Gardening
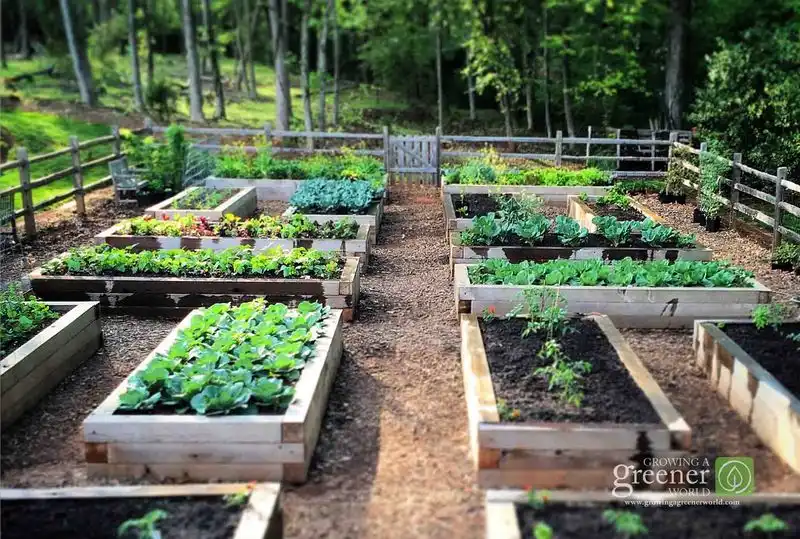

Raised beds offer numerous advantages, including improved drainage and soil quality. These structures warm up faster in spring, allowing for earlier planting and extended growing seasons.
Elevated beds also provide better control over soil conditions, making them ideal for areas with poor soil quality. This gardening method is adaptable to various environmental changes and helps prevent soil erosion. Raised beds are a versatile solution for those looking to enhance their garden’s resilience to climate fluctuations.
Cover Cropping for Soil Health
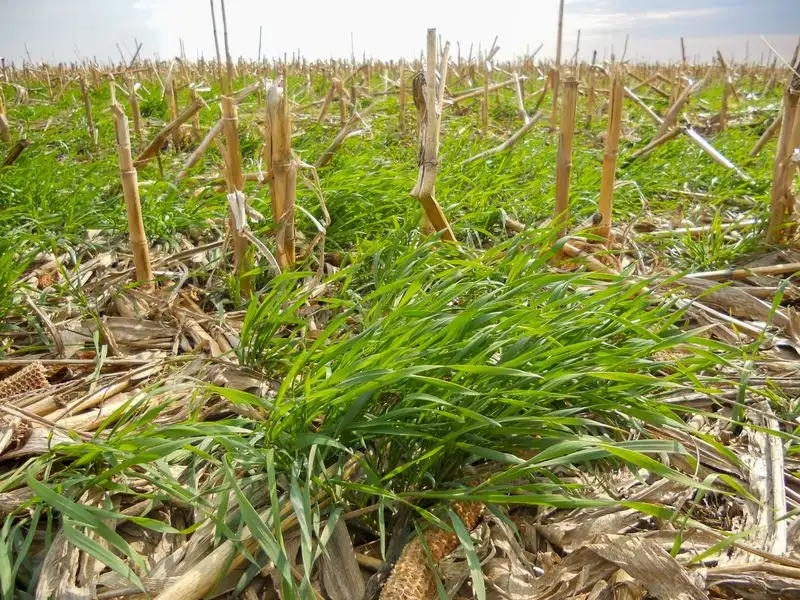

Cover crops like clover or rye are grown to enhance soil health during off-seasons. These plants prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility through organic matter addition.
Incorporating cover cropping into your gardening routine ensures that soil remains healthy and productive year-round. This practice not only enhances the immediate garden environment but also contributes to long-term sustainability. Cover crops are an integral part of climate-adaptive gardening, supporting robust plant growth in changing conditions.
Companion Planting Insights
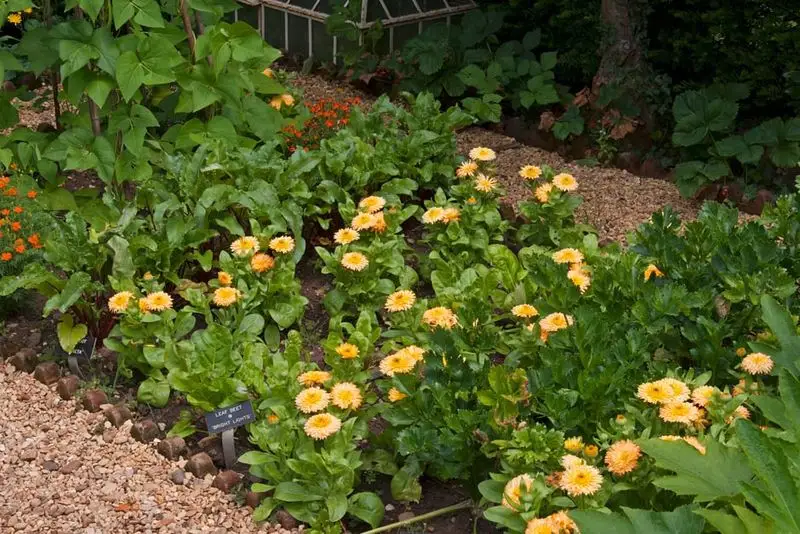

Companion planting leverages the natural relationships between plants to enhance growth and deter pests. Certain plant pairings, such as tomatoes with basil, can improve flavor and repel harmful insects.
By understanding these symbiotic relationships, gardeners can create a more resilient and productive garden ecosystem. This strategy reduces the need for chemical pesticides and fosters a healthier growing environment. Companion planting is a timeless practice that adapts well to modern gardening needs.
Mulching for Moisture Retention
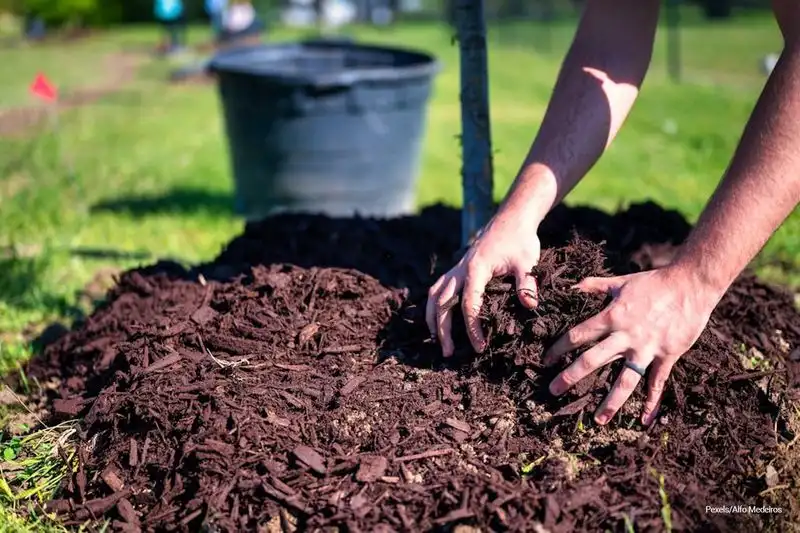

Mulching involves covering soil with organic materials like straw or wood chips to conserve moisture and regulate soil temperature. This technique reduces water evaporation and limits weed growth, making it a vital tool for climate-adaptive gardening.
By maintaining consistent soil moisture and temperature, mulching promotes healthier plant growth. It’s an efficient way to optimize water usage, especially in areas prone to drought. Mulching aligns with sustainable gardening practices, making it a key component of a resilient garden plan.
Rainwater Harvesting Techniques
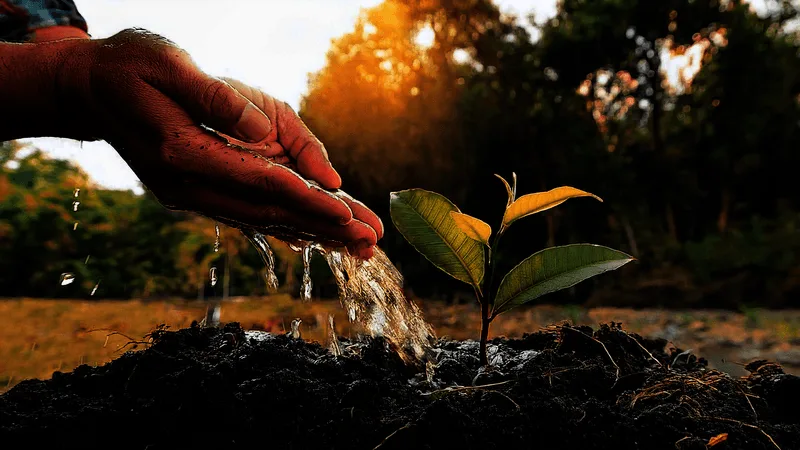

Collecting rainwater for garden use is both environmentally friendly and practical. By installing rain barrels or similar systems, gardeners can reduce dependence on municipal water supplies.
This technique ensures that water is available during dry spells, supporting consistent plant growth. Harvested rainwater is also free of chemicals, making it ideal for organic gardening. Rainwater harvesting is an effective strategy for water conservation and climate-adaptive gardening.
Season Extender Tools
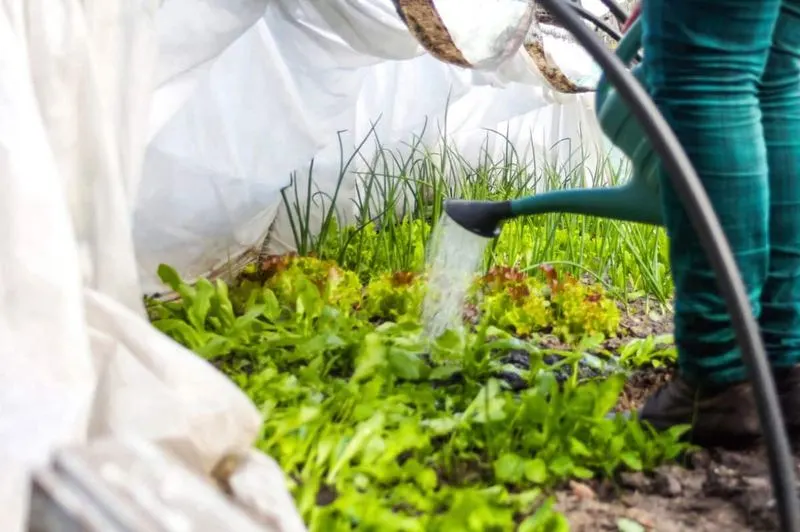

Tools like cold frames, row covers, and cloches allow gardeners to extend the growing season by protecting plants from extreme weather. These structures create microclimates that enable planting earlier in spring and harvesting later in fall.
By using season extenders, you can shield plants from frost and temperature fluctuations, ensuring a longer growing period. This adaptability is crucial in climates with unpredictable weather patterns. Season extenders are valuable assets for maximizing garden productivity.
Crop Rotation for Disease Prevention
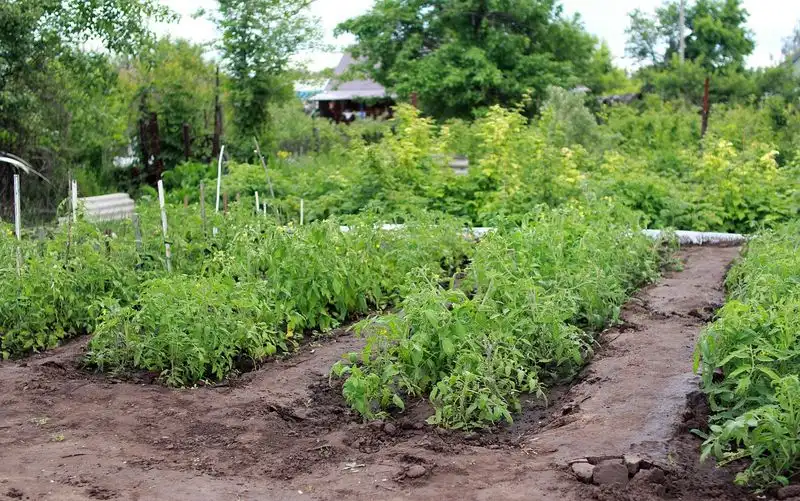

Rotating crops in the garden prevents disease buildup and maintains soil fertility by varying nutrient demands. This practice disrupts pest life cycles and reduces soil depletion, promoting healthier plants.
By planning crop rotations carefully, you can minimize the risk of soil-borne diseases and maximize nutrient availability. This technique is essential for sustainable gardening, balancing the needs of plants with the limits of the environment. Crop rotation is a foundational principle for maintaining a thriving garden.
Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
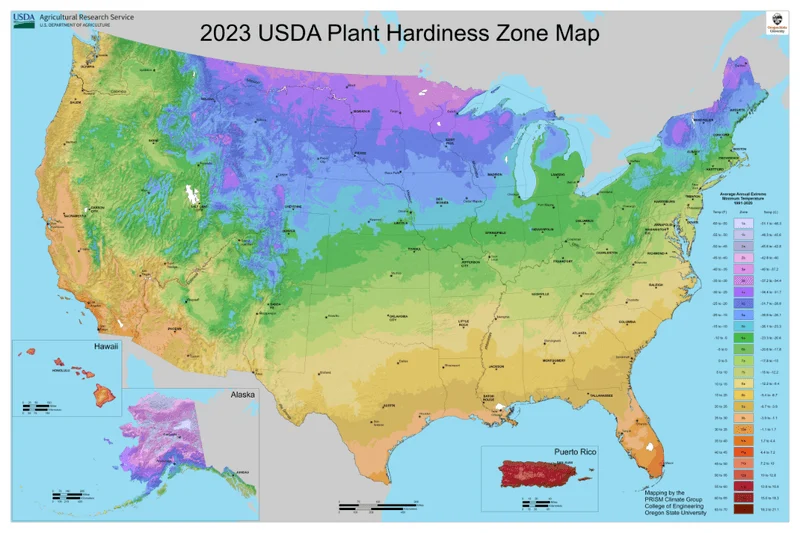
Plant hardiness zones provide valuable information about a region’s climate, helping gardeners select appropriate plants. By understanding these zones, you can choose species that will thrive in your local conditions.
This knowledge helps prevent the disappointment of planting unsuitable varieties that cannot withstand local temperature extremes. Hardiness zone information is a crucial tool for informed gardening, aligning plant choices with environmental realities. It’s a straightforward way to ensure the success of your garden in an ever-changing climate.
Adjusting Planting Depths
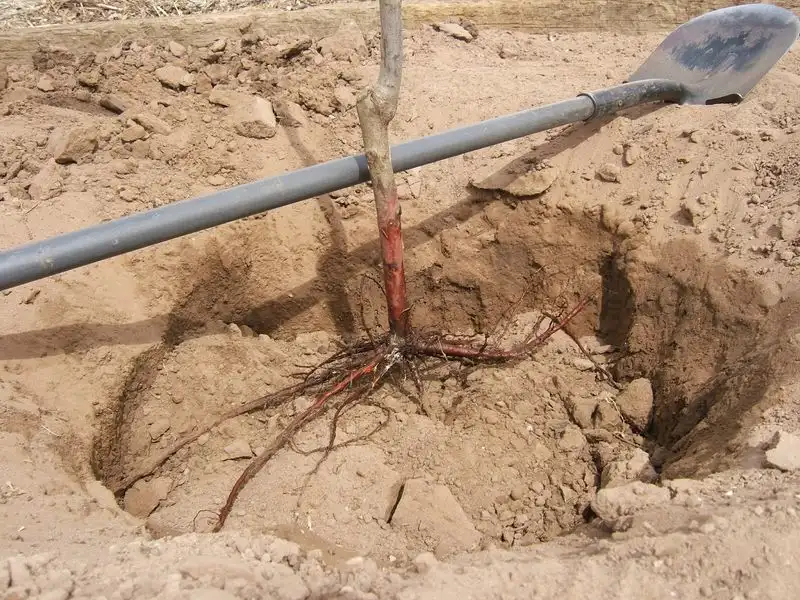

The depth at which seeds are planted can significantly affect germination and growth. Different plants have specific depth requirements, which can vary based on soil type and moisture levels.
By adjusting planting depths, gardeners can improve seedling emergence and resilience. This attention to detail ensures that each plant has the best possible start, adapting to both soil conditions and climatic changes. Proper planting depth is a nuanced but impactful strategy for optimizing garden success.

